Document Object Model
A Document Object Model commonly referred as DOM is the organization of elements in a web page. A web page consists of multiple elements such as a div, span, ul–li elements, input boxes, radio buttons, check boxes etc. These elements are organized in a particular order. Example, body will always be under html tag, an li will always be placed under a ul, an option will always be present under a select or a div inside another div, a span inside div etc.
Thus, a web page can be considered as the organization or hierarchy or tree of objects, which is called DOM. Every web page has a different DOM as compared to other page. A sample DOM for a web page can be represented as below. A DOM can also be referred as the structure of a web page.
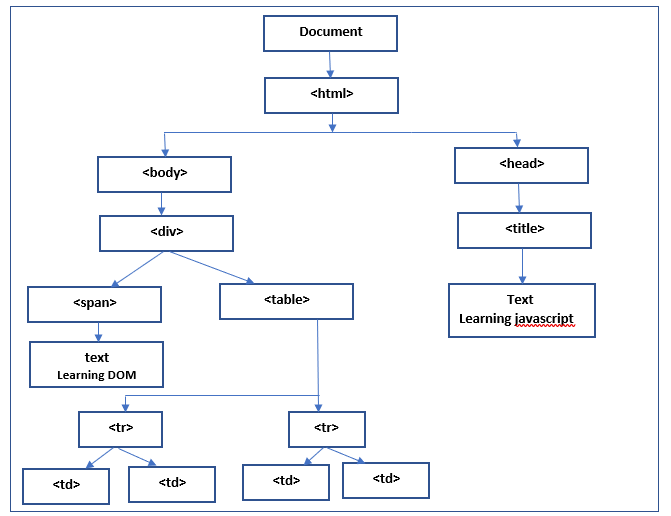
Web elements have many attributes such as id, name, class etc. They also are the part of DOM.
document Object
Javascript contains a document object which represents the entire web page. This document object contains all other elements. A document object can be used to access any element inside a web page. It can also be used to manipulate the DOM by adding and removing elements, hiding them, changing their text etc.
A document object is also a javascript object and thus, it has properties and methods just like a javascript object. These methods are used to perform the DOM manipulation task.
document Methods
Following are the commonly used methods which are used for DOM manipulation.
| Method | Working |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Takes the id of an element and returns that element. |
| document.getElementsByName(name) | Takes a string as argument and returns an array of all the elements having name attribute equal to that string. |
| document.getElementsByClassName(className) | Takes a string as argument and returns an array of all the elements having class attribute equal to that string. |
| document.getElementsByTagName(tagName) | Takes a string as argument and returns all the elements whose tag is equal to that string. |
| document.getRootNode() | Returns the root node of the DOM which is the document itself. |
Following are the commonly used methods which are used for DOM manipulation.
| Property | Working |
|---|---|
| document.body | Returns the body node of DOM |
| document.domain | Returns the domain of the current web page. Example, document.domain for current page will return “tutorials.codippa.com”. |
| document.head | Returns the head element of DOM. |
| document.title | Returns the title of web page. |
| document.URL | Returns the URL of the current web page. |
| document.lastModified | Returns the date and time the current web page was last modified. |
Following are the commonly used methods which are used for DOM manipulation.
| Method | Working |
|---|---|
| document.createElement(elementName) | Takes the string representing the tag of element to be created and returns the reference to that element. Example, document.createElement('span') |
| document.createTextNode(nodeText) | Takes a string as argument and creates a text node. This method is called after createElement method to add text to it and returns the reference to that node. Example, document.createTextNode('Javascript is fun') |
| appendChild(node) | Takes an element and adds it to the end of another element. This method is called on another element using .(dot) operator. When called on document object, it adds the new node to the document |
| document.renameNode(oldTag, nameSpace, newTag) | Used to change the tag of an element to the supplied tag. |
| removeChild(element) | Removed the child element from the element on which it is called |
An element can be added to DOM using first three methods from the above table. Example,
doc
// create a paragraph element
let para = document.createElement('p');
// create a text node
let textNode = document.createTextNode('Learning javascript');
// add text to paragraph
para.appendChild(textNode);
// add element to body
document.body.appendChild(para);