Arrays
What is a Go array
Array in Golang is a data structure that is used to store a collection of elements of same data type. An array is of a fixed size or length which is declared at the time the array is declared or initialized.
Array declaration
A Golang array is also a variable and is declared in the same way other variables are declared. Syntax of array declaration is
var array_name [size] data_type
where,
var is the keyword to declare a variable.
array_name is a user defined name which shall be used to access array elements.
size is an integer representing the total(or maximum) number of elements that the array will contain. Size should be enclosed between square brackets.
Size of array cannot be changed after array declaration.
data_type is the type of values that the array will contain.
Array declaration examples
Below are the valid examples of declaring an array.
// string array of 5 elements var names [5] string // integer array of 5 elements var numbers[5] int16 // float array with 5 elements var rates [5] float32
It is also possible to provide the size of the array as a Go constant or an expression. Example,
// declare a variable with value 5 const size = 5 // declare an array of 5 strings var names[size] string // declare two constants const min =0 const max = 5 // declare array with size as expression var numbers[min + max] int32
Size of array should be declared at the time of its creation, the size can be also provided as a constant value since it will not change once defined.
Array allocation
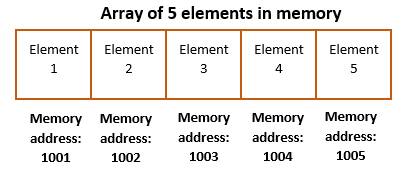
Array elements in Golang are stored in contiguous memory locations means all array elements are stored one after other and not randomly distributed in memory.
An array in Golang will be represented in memory as below.
Notice that the array elements are stored in adjacent memory addresses.
Accessing array elements
An array can be referenced using the name of its variable. Individual array elements are accessed using their index enclosed in square brackets.
Index of array elements is numeric with the first element at index 0, second at index 1 till the last element whose index is one less than the total number of elements in array.
Thus, syntax to access elements of an array is
array_variable[index_of_element]
Initializing array
Initializing array means providing value to its elements. There are two ways of setting values of array elements.
1. At the time of array creation
Initialize array elements at the time array is declared by writing values in curly braces as below.
var numbers = [5] int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Note that this way, the size and data type are to the right of assignment operator(=).
If you initialize elements at the time of declaring the array, then the size can be omitted since the compiler can interpret the total elements from values.
Thus, above declaration can also be written as
var numbers = []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
There is a short hand notation for initializing array which does not require var keyword as below.
numbers := [5]int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Again you can omit the size here as well since the compiler can figure it out from the number of elements.
numbers := []int{1, 2, 3, 4 ,5}
2. Initializing individual elements
Access each array element using its index and assign it a value as below.
var numbers [5] int numbers[0] = 10 numbers[1] = 20 numbers[2] = 30 numbers[3] = 40 numbers[4] = 50
This method is not feasible for large arrays so you can use a for loop to initialize elements as below.
var numbers[] int
for i:=0; i < 5; i++ {
numbers[i] = i
}
Getting values of elements
Array elements can be accessed using numeric indexes. Array variable followed by the index of an element will return the value stored at that index.
This value can be used directly in an expression or assigned to a variable of same type as the array. Example,
var num1 = 10 // assigning array element to a variable var num2 = numbers[0] // using array element in expression var sum = num1 + num2 + numbers[1]
If you try to assign an element from int array to a string variable, then you will get an error
cannot use arr[0] (type int) as type string in assignment
Modifying array elements
It is possible to change or assign value to an array element after the array is created. Write array variable and index of element at the left and the value to assign at the right of assignment operator(=). Example,
numbers := []int{10, 12, 30}
// update second element
numbers[1] = 20
Again, the type of value assigned should match the type of array.
Array length
Length of an array is the count of elements present in the array. Length is also referred as the size of array. It is an integer value and to know the length of array, use len function providing it the array as argument. Example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var arr [5]int
fmt.Println("Count of elements of array is ", len(arr))
}
which prints
Count of elements of array is 5
Previous Article
Loops
Next Article
Zero value
Arrays
What is an Array?
An array is a collection or a list of similar items logically grouped together.
Similar items means values which represent a particular type of entity.
Examples are names of car companies, list of car models, laptop types, smartphone brands etc.
Similar items in above definition does NOT mean those which have the same data type such as a list of strings, list of numbers or a list of boolean values.
A single array in javascript can contain a string, an integer, a decimal value, an object and an array also. Thus, array in javascript is just a logical group of values.
Array Syntax
A javascript array is surrounded by square brackets (‘[‘ & ‘]’).
Elements of the array are separated by a comma(,). An array is assigned to a variable which becomes the name of the array.
Name of variable is user defined. It is not mandatory to assign an array to a variable but you have to do it if you want to use it anywhere else.
Thus, an array looks like
var cars = ['Honda', 'Hyndai', 'BMW', 'Audi']; var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; //different data types var hybrid = [1.2, 'string', true, 24]; //array inside array var ramSizes = [8, 16, 32, 64]; var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo', ramSizes];
How to create an Array
There are 2 ways to create an array
- Using array literal
Create 2 enclosing square brackets, place the array values inside them and assign it to a variable. Just as shown in examples above. Simple as that.var arrayName = [element1, element2, …..];
- Using new keyword
Using this approach, an array can be created using the below syntaxvar arrayName = new Array(element1, element2, ….);
We are creating an array object using its constructor. Syntax is similar to previous approach but is not the preferred way.
Elements can be of any type as in earlier approach.If you provide a single numeric argument to the constructor, then it is considered as the size of the array.
That is,var arrayName = new Array(5)will create an array of 5 elements and not an array with a single element whose value is 5.
Thus, in order to create array with this approach and add elements to it, 2 statements are required.
[the_ad id=”94″]
Adding elements to Array
Javascript arrays have a push method which allows you to add elements to an array.
It takes the element to add as argument and adds the element to the end of array.
push returns the length of the array. Also, more than 1 elements may be added to the array using push method. Example,
var evenNumbers = [0, 2, 4, 6]; evenNumbers.push(8); // array becomes [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] var length = evenNumbers.push(10, 12, 14); // length will be 8
push returns the length of the array after the element is added.
Accessing Array Elements
Array elements are index based(index starts at 0) and its elements can be accessed using indexes. Syntax to access an array element is :
var element = arrayName[ elementIndex];
Thus, to access first element of an array, following syntax is used
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; var l = laptops[1]; // This returns Sony
[the_ad id=”95″]
Iterating over Array
A javascript array can be iterated using a for loop.
Since array indexes start at 0, the loop starts from 0. Also, array has a length property which returns the total number of elements in the array.
Thus, the last element of the array will have index = length – 1.
Therefore, to iterate over an array, a for loop starting from 0 to length – 1 can be used.
Example,
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
for (var index = 0; index < laptops.length; i++) {
console.log('Laptop : '+laptops[index]);
}
In order to iterate over an array for...of loop can also be used. It is a newer feature in javascript.
Syntax is:
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
for (let lappy of laptops) {
console.log('Laptop : '+lappy);
}
let followed by a name declares a variable. In each iteration, this variable contains the current array element.
Common Array Methods
Following are the commonly used javascript array methods
| Method | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| push | Used to add an element to array.(Has been discussed above) | |
| toString | Converts an array to a string of comma separated values |
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops.toString(); // returns Dell, Sony, Lenovo
|
| pop | Returns the last element of the array. The element is also removed from the array. |
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops.pop(); //returns Lenovo // array is now ['Dell', 'Sony']
|
| shift | Returns the first element of the array. The element is removed from the array and all the remaining elements are shifted towards the left. |
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops.shift(); //returns Dell // array is now ['Sony', 'Lenovo']
|
| join | Returns a string combined with a separator. The separator is passed as an argument to this method. |
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
laptops.join(' & ');
//returns Dell & Sony & Lenovo
|
| unshift | This method is opposite of shift method. It adds an element to the beginning of the array and shifts other elements to the right. The element to be added is passed as an argument to this method. This method returns the new length of the array. |
var laptops = ['Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
laptops.unshift('Apple'); //returns 4
// array is now ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']
|
| slice | Accepts two integers as arguments and returns the array of elements whose indexes lie in between the two arguments. Note that the indexes are zero-based and array elements till (second argument – 1) are considered. |
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops = laptops.slice(1,2); // returns ['Dell']
|
| sort | This method sorts an array in alphabetical order. If the array is of numbers, then it sorts the array from low to high values. |
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops.sort(); // returns ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Lenovo', 'Sony'];
|
| reverse | Reverses the elements of the array. That is, last element becomes the first, second last becomes the second element and so on. |
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops.sort(); // returns ['Lenovo', 'Sony', 'Dell', 'Apple']
|
| indexOf | This method accepts an array element as argument and returns the index of that element inside the array. It returns -1 if the element does not exist in the array. This method can be used to check if an array contains an element. |
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
laptops.indexOf('Dell');
// returns 1
|
[the_ad id=”267″]
How to recognize Array
Suppose you want to test whether a given variable represents an array or not.
One will suggest to use typeof operator.
But the problem is that typeof used on array will return “object“. This is because an array is also an object.
So, the question is how to tell whether a variable represents an array. Following methods will be useful in this case.
Method 1 : Using instanceof operator
instanceof operator used on array variable will return true if the variable is an array, false otherwise. Example,
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; laptops instanceof Array //will return true
Method 2 : Using isArray method
Array object defines a method isArray which takes an argument which will return true if the argument is an array, false otherwise. Example,
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo']; Array.isArray(laptops); // returns true var value = 5; Array.isArray(value); // returns false Array.isArray(new Array()); // returns true Array.isArray(); // returns false
This method was introduced in ECMAScript 5 and will not work in older browsers.
[the_ad id=”86″]
Method 3 : Using constructor property
Array variable has a constructor property. This property returns the function name which created the array.
Converting the value to a string using toString method returns a string representation of this function.
Now, whether the variable is an array can be tested by checking the presence of “Array” in this string.
Example,
var laptops = ['Apple', 'Dell', 'Sony', 'Lenovo'];
var functionName = laptops.constructor; // returns Array()
var functionStr = functionName.toString(); // returns function Array() { [native code] }
var isarray = functionStr.indexOf("Array") > -1; // returns true
Previous Article
Variables
Next Article